Overview
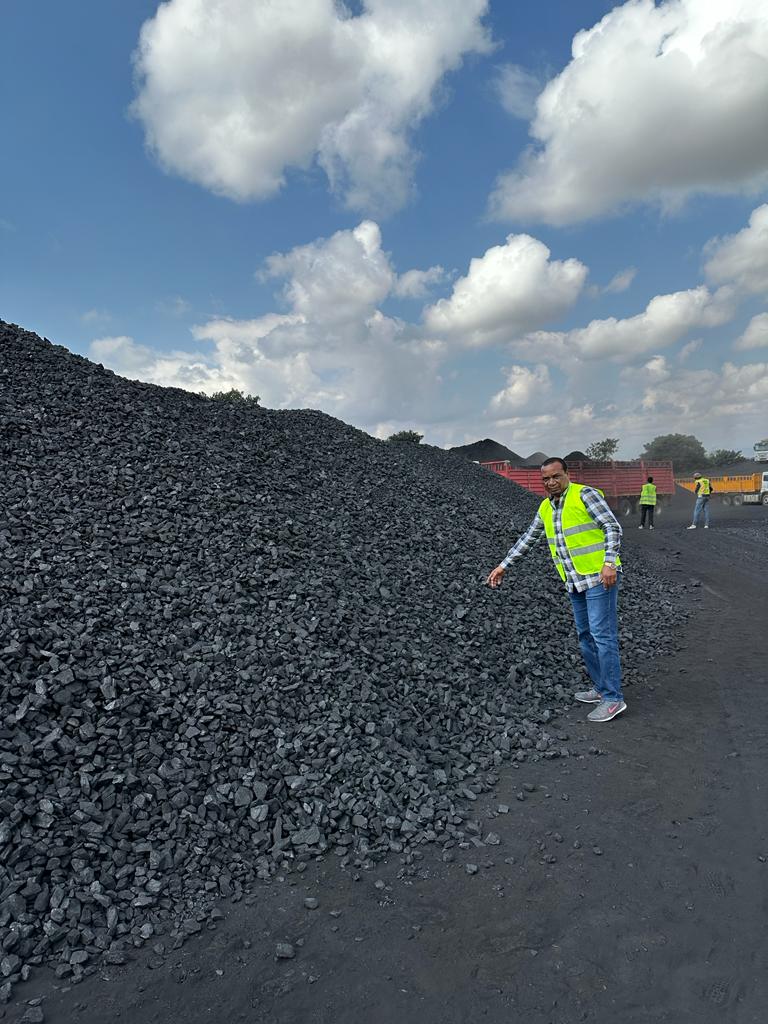
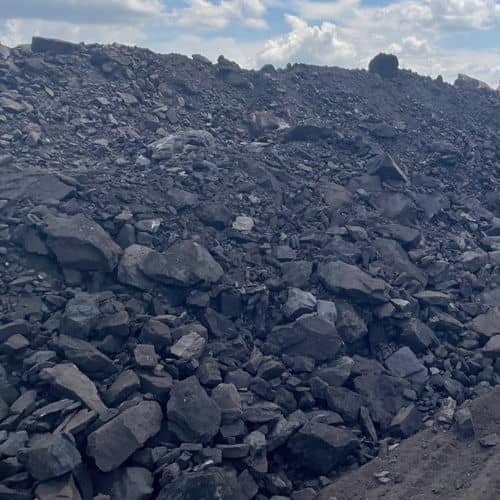
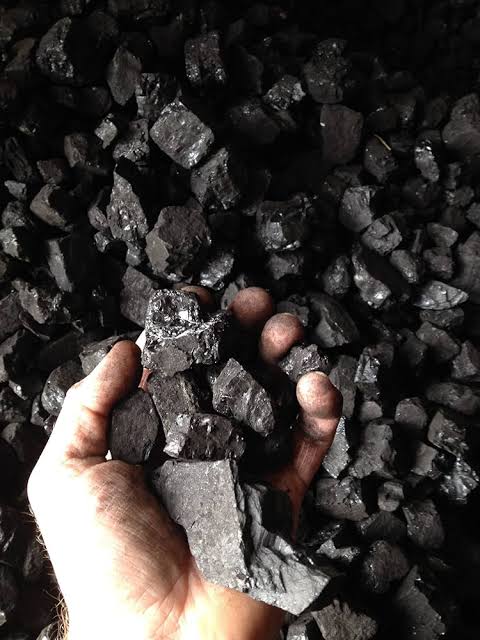
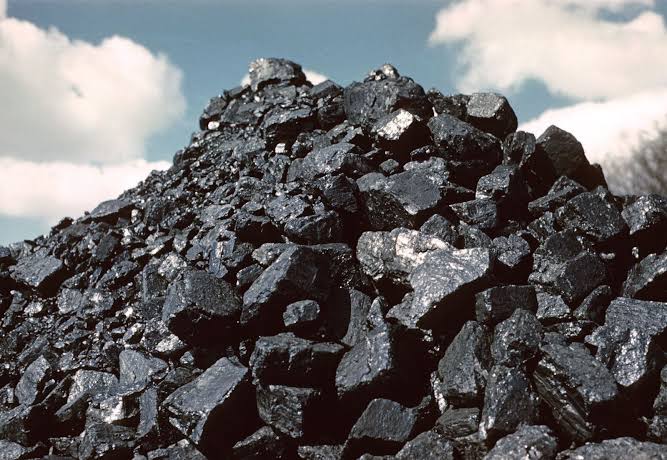
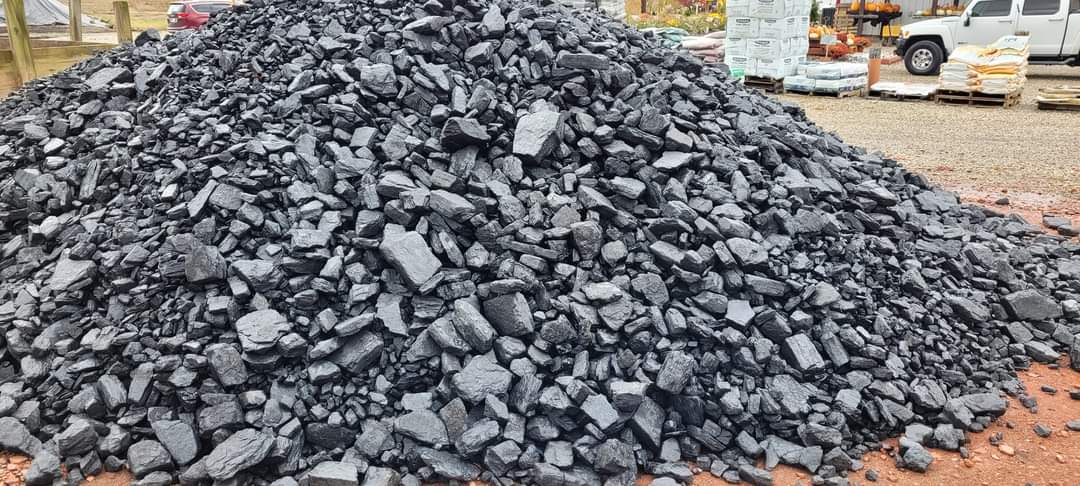
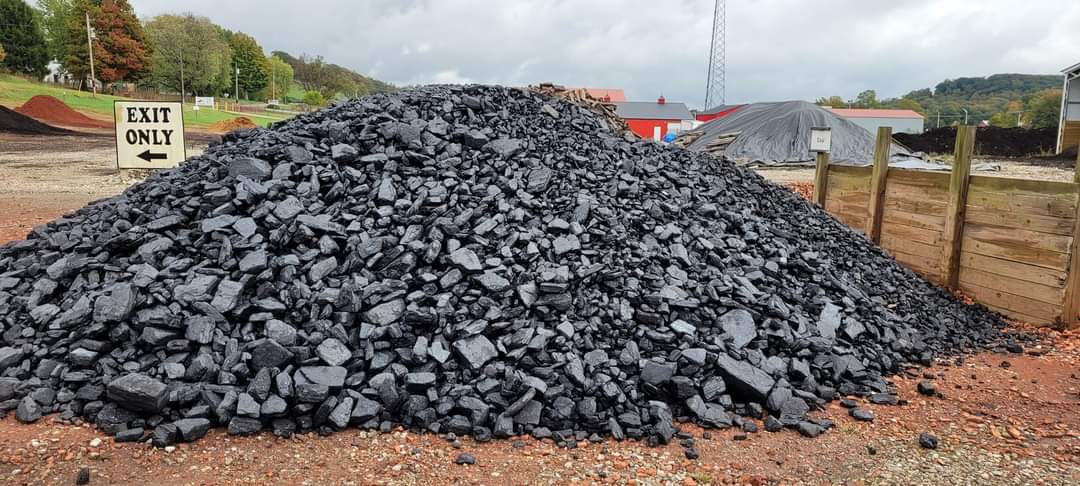
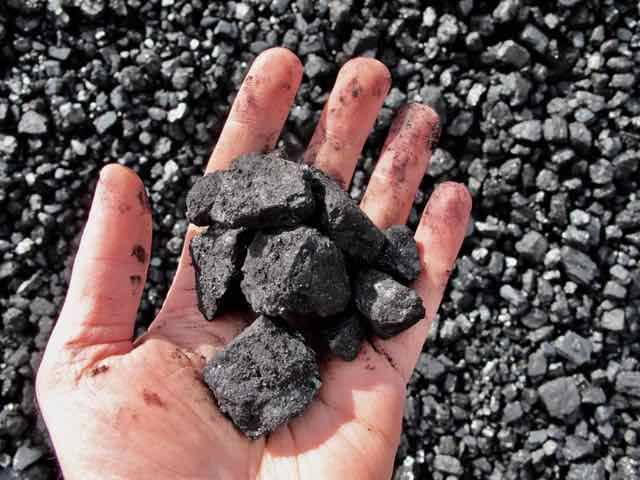
Bituminous coal, often referred to as black coal, is a dense, hard, and friable type of coal that contains bitumen—a tar-like substance. Known for its rich color and quality, bituminous coal serves as a crucial resource for a variety of industrial applications, particularly in energy and steel production.
Color
Bituminous coal typically displays a striking black or deep dark-brown color. Its surface often features alternating bands of bright and dull material, which contribute to its unique appearance and make it distinguishable from other types of coal.
Formation
This type of coal is formed through the natural transformation of sub-bituminous coal, which, over time, is subjected to increased heat and pressure. When buried deeply and heated to a minimum of 185°F, the coal undergoes physical and chemical changes, developing into the harder, more energy-dense bituminous form.
Uses
Due to its high carbon content and energy efficiency, bituminous coal has widespread applications:
- Electricity Generation: Power plants use bituminous coal as a primary fuel source to generate electricity.
- Steel Industry: In steel manufacturing, bituminous coal is a key component in coke production, which is essential for smelting iron ore.
Quality
Bituminous coal ranks above lignite and sub-bituminous coal in terms of quality. It offers higher energy content and greater efficiency, making it a preferred choice for industries that require reliable, high-quality fuel for their operations. Its characteristics make it a more durable and efficient option compared to lower-grade coals.


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.